GDP
Germany's troubled economy shows modest growth after two years of shrinkage
Germany’s economy returned to modest growth last year after two consecutive years of contraction, official data showed Thursday, raising expectations that government investment in infrastructure and defense could help break years of stagnation.
The country’s gross domestic product (GDP) grew by 0.2% in 2025, driven by stronger consumer and government spending, while exports remained subdued due to tougher U.S. trade policies under President Donald Trump, the German Federal Statistical Office reported. This followed GDP contractions of 0.5% in 2024 and 0.9% in 2023.
“Germany’s export sector faced significant headwinds from higher U.S. tariffs, a stronger euro, and growing competition from China,” said Ruth Brand, head of the statistics office, in a statement.
Looking ahead, analysts expect slightly stronger growth this year as Chancellor Friedrich Merz’s government ramps up infrastructure spending to address years of underinvestment. Defense expenditure is also rising amid heightened security concerns following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Read more: Germany to increase its funding contribution to Saidabad WTP Phase III project
Germany has faced extended economic stagnation since the COVID-19 pandemic. Rising energy costs from the Ukraine war, growing competition from China in key sectors such as automobiles and industrial machinery, higher tariffs on EU goods imposed by the U.S., and a stronger euro have all weighed on the export-driven economy. Structural challenges, including bureaucratic hurdles and a shortage of skilled labor, have also constrained growth.
Preliminary data indicate that the German economy expanded by 0.2% in the final quarter of 2025. A group of leading economists has projected 0.9% growth for 2026, though they caution that slower-than-expected government spending could limit the recovery.
1 month ago
Bangladesh’s GDP growth rises to 4.5% in Q1 of FY2025–26
Bangladesh’s economy posted a stronger performance in the first quarter (Q1) of the 2025-26 fiscal year, with gross domestic product (GDP) growth accelerating to 4.50 percent on a point-to-point basis in constant prices, according to provisional estimates.
The latest quarterly figures show a notable improvement compared to the same period of the previous fiscal year, when GDP growth stood at 2.58 percent, reflecting a broad-based recovery driven mainly by the industrial sector alongside improvements in agriculture and services.
In current prices, the size of GDP in Q1 of FY26 has been estimated at Tk 13,853,433 million (Tk 13,853 billion), up from Tk 12,401,032 million (Tk 12,401 billion) recorded in the first quarter of FY25, indicating a substantial expansion in nominal economic activity year-on-year.
According to quarterly-based estimates, the growth rate of gross domestic product at constant prices for the entire FY25 has been placed at 3.72 percent.
Read more: Bangladesh sees $1.12bn in remittances in first 10 days of January
The Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS) noted that this quarterly-based estimate differs from the provisional annual GDP estimate for FY25 prepared on a yearly basis.
The discrepancy will be addressed through internationally accepted benchmarking methods once the final annual GDP figures for FY25 are compiled, ensuring consistency between quarterly and annual national accounts.
The agriculture sector returned to positive territory in Q1 of FY26, registering a growth of 2.30 percent at constant prices on a point-to-point basis.
This marks a significant turnaround from the contraction of 0.60 percent recorded in the same quarter of FY25.
The improvement in agricultural output suggests a degree of stabilisation following earlier disruptions, supported by better crop performance and a gradual recovery in allied activities such as livestock and fisheries.
The rebound in agriculture is expected to provide some relief to rural incomes and food supply dynamics.
The industrial sector emerged as the strongest performer, posting a robust growth of 6.97 percent in Q1 of FY26, nearly double the 3.59 percent growth recorded in the corresponding quarter of the previous fiscal year.
Analysts view the sharp acceleration in industrial growth as a key driver of the overall economic upturn, reflecting improved manufacturing activity, gradual easing of energy-related constraints and a modest pickup in domestic demand.
Export-oriented industries, particularly manufacturing, are believed to have contributed significantly to the sector’s stronger performance.
Bangladesh’s GDP growth slows to 3.97% in FY2024–25
The services sector also recorded improved growth, expanding by 3.67 percent in Q1 of FY26 compared to 2.96 percent in the same quarter of FY25.
The expansion in services indicates a gradual revival in trade, transport, communications and other service-related activities, which had remained under pressure amid economic uncertainty and subdued consumption in the previous year.
The stronger GDP growth in the first quarter of FY26 points to early signs of economic recovery, supported by improved sectoral performance across agriculture, industry and services.
However, economists caution that sustaining this momentum will depend on continued policy support, stability in the macroeconomic environment and progress in addressing structural challenges.
The provisional nature of the quarterly estimates also underscores the need for careful interpretation, with revisions expected as more comprehensive data become available.
Nonetheless, the Q1 figures provide an encouraging signal at the start of the fiscal year, suggesting that growth is gradually gaining pace after a period of slowdown.
Read more: Forex reserves hit 3-year high as December remittances cross $3bn
1 month ago
Bangladesh economy falters; growth slows, factories shut, jobs lost
Bangladesh’s economy is under growing pressure as GDP growth slows, foreign investment declines and unemployment rises, raising concerns among economists and industry insiders that the economy could face long-term instability without urgent reforms.
According to the latest World Bank report, GDP growth for the current fiscal year may drop to 3.3 percent, the lowest in two decades.
At the same time, the Ministry of Finance reports that foreign investment fell by over 70 percent in the first six months of FY2024-25.
The World Bank’s April publication ‘Bangladesh Development Update’ warns that by 2025, an additional 3 million people may fall into poverty, driven by weak investment and growing internal challenges.
Dr Anu Muhammad, a former professor of economics at Jahangirnagar University, said public frustration is rising due to prolonged economic difficulties.
“After the fall of the Awami League, many corrupt business groups and money launderers fled. That was a major opportunity to restructure the economy, but it was missed. The same pattern of economic management continues, and it has yielded no positive results,” he said.
Industrial Police data shows nearly 100 factories in Gazipur, Narayanganj-Narsingdi and Savar-Dhamrai have shut down permanently, leaving more than 60,000 workers unemployed.
Economy eyes gradual growth with steady recovery in key sectors: Finance Ministry
Investigations reveal that many investors during the Awami League regime are now in jail, have gone into hiding or fled the country. Due to lack of funds and fewer purchase orders, these factories were forced to cease operations.
“More than a hundred factory closures have rendered hundreds of thousands unemployed,” Dr Anu Muhammad added. “Many who fled after closing factories had enjoyed undue privileges during the previous government. While the beneficiaries should be held accountable, not ensuring alternatives for the workers shows poor judgement. This will have a direct impact on the economy.”
Instead of focusing on increasing national capacity, the proposed national budget appears to raise dependence on imports. Ignoring domestic industries and relying on foreign imports will deepen the crisis, the economist observed.
Cash flow continues to decline in factories still in operation, coupled with an energy crisis. Shortages in fuel supply relative to demand and limited bank financing are bringing uncertainty to the industrial sector.
Ashraf Ahmed, Director of the Dhaka Chamber of Commerce and Industry (DCCI), said, “Running factories with imported LNG are becoming extremely difficult. Most factories are suffering due to fuel shortages. When production drops, the economy suffers directly. From 2012 to 2022, private sector credit flow was strong. Now that flow has weakened. Factory owners have no capital, production has stalled, workers are not getting paid, and the economy is spiralling into disorder.”
He added, “Although law and order has improved somewhat, other sectors remain unstable. Many banks are now so weak they cannot provide funds to businesses. At the same time, borrowing at high interest rates of around 16 percent makes doing business highly risky.”
Industry representatives said gas shortages have halved production in many factories. To address this, the Energy Division is planning to increase LNG imports. Yet, with no new gas fields discovered and growing reliance on imported LNG, the situation is worsening. Bangladesh’s failure to explore the potential of 26 offshore blocks in the Bay of Bengal has added to the problem.
A senior Petrobangla official, requesting anonymity, said, “During the Awami League regime, international tenders were floated, but no company showed interest. The new government extended the bidding period, but still received no response. There is little hope of extracting energy from the Bay of Bengal anytime soon.”
Towfiqul Islam Khan, Senior Research Fellow at the Centre for Policy Dialogue, said, “Without political stability, attracting foreign companies will remain difficult. With elections approaching, no company will commit to a new agreement without policy guarantees. The government should provide a clear election roadmap and reach an understanding with political parties.”
Khan stressed that regardless of any constitutional or electoral reform, the government must address the pressing issue of 2.1 million people who lost jobs in the past 10 months – 1.8 million of whom are women.
Govt now focused on laying strong foundation of economy: Finance Adviser
Mohammad Helal Uddin, Executive Vice Chairman of the Microcredit Regulatory Authority, said the current problems with investment, banking and energy are the result of longstanding mismanagement during the previous government.
He said those now interested in investing are proceeding cautiously. The direction of future investments will depend on the policies of the post-election government.
According to him, the economic missteps of the Awami League era will continue to take a toll in the coming months.
8 months ago
TIB findings: Over 70 percent of households partake in corruption
The Transparency International (TIB) findings revealed in household surveys since 2010 show that from 2009 to April 2024, the included service sector institutions have collected an estimated total of Tk 146,252 crore in bribes.
The households that paid bribes or unauthorized money for services from May 2023 to April 2024 spent an average of Tk 5,680 each. The total estimated bribes or unauthorized payments across all sectors during this period amounted to Tk10,902 crore, which is 1.44 percent of the national budget for 2023-24 and 0.22 percent of GDP.
EuroCham launched, seen as new milestone in Bangladesh-EU business relations
The passport, BRTA, law enforcement, judiciary, and land sectors were found to be the most corrupt in the service sector, with 70.9 percent of Bangladeshi households reporting corruption between May 2023 and April 2024.
Furthermore, 50.8 percent of households experienced bribery at this time, with law enforcement, BRTA, and passport services having the highest percentages. TIB revealed these findings at a press conference unveiling the “Corruption in Service Sectors: National Household Survey 2023” results.
The survey of 2023 revealed that 70.9 percent of households in Bangladesh has experienced corruption in some form while availing services from various public and private sectors or institutions. Passport services 86 percent were identified as the most corrupt sector, followed by BRTA 85.2 percent, law enforcement agencies 74.5 percent, judicial services 62.3 percent, land services 51 percent, public healthcare 49.1 percent, and local government institutions 44.2 percent. Overall, 50.8 percent of households reported paying bribes or being forced to pay unauthorized money to access services.
The highest incidences of bribery were reported in passport services 74.8 percent, BRTA 71.9 percent, law enforcement agencies 58.3 percent, judicial services 34.1 percent, land services 32.3 percent, and local government institutions 29.7 percent.
Among the households that paid bribes, 77.2 percent cited the reason as “services cannot be obtained without paying a bribe,” highlighting a concerning institutionalization of bribery practices.
Tensions between Bangladesh and India grow over attack on Agartala mission
The survey collected data on corruption and harassment encountered by selected households while obtaining services from service sectors between May 2023 and April 2024. Data for this survey were collected between May 13 and August 3, 2024.
1 year ago
Interim Government to implement new 'Statistics Policy' amid allegations of data manipulation by BBS
The interim government of Bangladesh is moving to establish a comprehensive 'Statistics Policy' to address longstanding concerns about inaccuracies in data published by the Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS). This initiative follows widespread allegations that the BBS had provided misleading economic data under the previous Awami League government.
During the Awami League's tenure, the BBS was repeatedly accused of inflating GDP growth figures while downplaying inflation, raising serious doubts about the credibility of the country’s official statistics.
Interim Government committed to curbing essential commodity prices by breaking syndicates: Mahfuj Alam
“We are working to formulate a Statistics Policy, which will soon be approved by the Advisory Council,” said Planning Adviser Dr. Wahiduddin Mahmud at a recent press briefing following an ECNEC (Executive Committee of the National Economic Council) meeting. He emphasized the need for a clear, unified approach to ensure the accuracy and integrity of national data.
BBS Under Scrutiny
The BBS, which operates under the Ministry of Planning, faced consistent criticism for its inability to provide reliable data. Their capacity is not as strong as statistical institutions in other developing countries, Dr. Wahiduddin said. He pointed out that political pressure had influenced the BBS's economic data, particularly during periods of economic growth and inflation reporting.
Sources within the Planning Commission and BBS confirmed that the agency struggles with capacity issues, making it difficult to collect and analyze accurate data. Furthermore, political interference has been a significant obstacle, particularly concerning key economic indicators such as GDP and inflation.
Acknowledging these challenges, Dr. Wahiduddin reiterated his commitment to maintaining the independence of the BBS. “I have already informed them that I will not intervene in their reports, regardless of any shortcomings. The data, whether high or low, must stand on its own merit,” he said.
NBR focuses on boosting low tax-to-GDP ratio as major business figures come under scrutiny
Strengthening the BBS’s Capacity
Dr. Wahiduddin, a well-known economist, has stressed the importance of empowering the BBS as an independent entity. He aims to enhance its ability to provide unbiased and accurate data without external interference. Discussions with officials from both the Planning Commission and BBS indicate a strong focus on capacity-building initiatives to improve the bureau's performance.
The BBS is currently the sole national statistical office in Bangladesh, responsible for generating and publishing critical data on population, agriculture, industry, and the broader economy. However, under past administrations, its activities were often governed by orders and circulars, lacking a cohesive policy framework.
Future Reforms
The BBS gained legal grounding through the passage of the 'Statistics Act' on February 27, 2013, which formally outlined its responsibilities. According to this law, the bureau is tasked with producing accurate and timely statistics, conducting national censuses, and delivering data that meets the needs of policymakers, researchers, and other stakeholders.
However, the policy aims to modernize these functions and address gaps in the existing system. Among the bureau’s future tasks will be updating the National Strategy for the Development of Statistics, standardizing statistical programs to international standards, and implementing a National Data Bank.
The implementation of the Statistics Policy is expected to mark a significant step toward bolstering the integrity of Bangladesh’s statistical system, ensuring that data-driven decisions can be made with confidence.
Inflation decreases by 1.17 % in August: BBS
1 year ago
Parliament passes national budget for FY 2024-25 targeting GDP growth at 6.75pc, inflation at 6pc
The parliament of Bangladesh on Sunday (June 30, 2024) passed the Tk 797,000 crore national budget for FY 2024-25 setting the goal of economic growth at 6.75 percent and keeping annual inflation at around 6 percent.
Finance Minister Abul Hassan Mahmood Ali moved the Appropriations Bill 2024, seeking a budgetary allocation of Tk 12,41,752 crore which was passed by voice votes.
Earlier on Saturday, the parliament passed the Finance Bill 2024 with some minor changes.
Following the proposal mooted in the House by the Finance Ministry for the parliamentary approval of the appropriation of funds for meeting necessary development and non-development expenditures of the government, the ministers concerned placed justifications for the expenditure by their respective ministries through 59 demands for grants.
Read more: Proposed budget has high hopes, and low direction to achieve goals: RAPID
Earlier, the parliament rejected, by voice votes, a total of only 251 cut-motions that stood in the name of opposition members on 59 demands for grants for different ministries.
A total of seven MPs, including from Jatiya Party Mujibul Huq, Hafiz Uddin Ahmed, and Independent MP Pankaj Nath, Md Hamidul Haque Khandker, Md. Abul Kalam, Md Suhrab Uddin and Md. Nasser Shahrear Zahedee placed the cut motions.
They were, however, allowed to participate in the discussion on Law Ministry, Secondary and Higher Studies Division and Social Welfare Ministry.
Later, Speaker Shirin Sharmin Chaudhury quickened the process of passing the demands for grants for different ministries without giving a lunch break.
Opposition and independent MPs were present in the House when the Appropriation Bill was passed, and they did not raise objection to passing the bill.
Read more: Finance Bill 2024, entailing budget for next fiscal, passed in Jatiya Sangshad
1 year ago
Bangladesh 3rd most peaceful country in South Asia: 2024 Global Peace Index
Bangladesh has secured the third position in the South Asia region on the 2024 Global Peace Index (GPI), according to the latest report by the Institute for Economics & Peace (IEP).
Bangladesh ranks 93rd globally with an overall score of 2.126, reflecting a slight deterioration in peacefulness from the previous year.
South Asia is the third least peaceful region globally, ahead of only the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) and sub-Saharan Africa. The region experienced a minor decline in peacefulness over the past year, with four of the seven countries recording deteriorations in their overall scores. The primary driver of this decline was an increase in military expenditure as a percentage of GDP and a reduction in payments for UN peacekeeping funding since 2012.
Despite these challenges, there were improvements in the Ongoing Conflict and Safety and Security domains across the region.
Read more: Bangladesh ranks 141 out of 164 on the Freedom Index
Bhutan emerged as the most peaceful country in South Asia, maintaining its top position since 2011 and ranking 21st globally. Bhutan also recorded the largest increase in peacefulness in the region, improving its overall score by 2.6 percent.
In contrast, Afghanistan remains the least peaceful country in the region, ranked 160th globally. Afghanistan's peacefulness deteriorated due to increases in militarization and safety and security concerns, although some indicators have shown significant improvements in recent years.
India, the largest country in South Asia, improved its overall peacefulness by 1.6 percent over the past year, achieving its highest level of peacefulness since the inception of the index. The improvement was mainly due to a reduction in the intensity of internal conflicts, particularly in the border regions.
The 2024 GPI, now in its 18th edition, ranks 163 independent states and territories based on their level of peacefulness, covering 99.7 percent of the world's population. The index is widely regarded as the leading measure of global peacefulness, offering a comprehensive analysis of trends in peace, its economic value, and strategies for developing peaceful societies.
Read more: US says it will remain Bangladesh’s steadfast partner in Rohingya refugee response
1 year ago
Mitigating deficit: Govt targets external financing of Tk 1200.3 billion and Tk 1306.4 billion over next two fiscals
In an effort to promote a robust domestic debt market, the Bangladesh government is strategizing to increase its share of marketable securities in the coming years. According to a recent Finance Ministry document, the administration is also committed to continued issuance of Islamic securities Sukuks but has currently shelved plans for Eurobond issuances on the global market.
As fiscal deficits loom, with projections showing a deficit of Tk 2792.3 billion for FY 2024-25 and Tk 3170.7 billion for FY 2025-26—equating to 5% of GDP each year—the government underscores the need for strategic domestic borrowing.
The focus remains on minimizing borrowing costs through traditional external creditors, which are preferred, the document detailed.
The strategy for addressing deficits includes an ambitious target of collecting Tk 1200.3 billion from external sources in FY 2024-25 and Tk 1306.4 billion in FY 2025-26, each constituting 2.1% of GDP.
Domestic sourcing is expected to contribute significantly more, with plans to collect Tk 1677.7 billion and Tk 1864.4 billion over the same periods, representing 2.9% of GDP.
UK's BII supports MSMEs, women entrepreneurs in Bangladesh with $50m debt commitment to BRAC Bank
Significantly, the banking sector is anticipated to contribute Tk 1384.9 billion in FY 2024-25 and Tk 1547.3 billion in FY 2025-26. In comparison, non-banking sectors will contribute Tk 292.8 billion and Tk 317.1 billion respectively.
Savings certificates will add Tk 191.4 billion and Tk 190.3 billion, while other sources are projected to contribute over Tk 100 billion annually.
The government maintains a prudent deficit financing policy to stave off debt distress, keeping the deficit steady at around 5% of GDP and maintaining a stable debt level at around 33% of GDP in recent years, the finance ministry document explained. This balanced approach aims to mitigate the risks associated with deficit financing while prioritizing sustainable economic development.
In terms of the medium-term outlook, the government expects domestic borrowing to remain stable at 2.9% of GDP. However, the approach to marketable securities will see a significant nominal increase, with a planned reduction in the reliance on higher-cost National Savings Certificate instruments, which will see a gradual decrease in their contribution to the financing mix.
External financing is also projected to increase nominally between FY 2023-24 and FY 2025-26, driven by greater disbursement for large projects and increased budget support, though dependent on the pace of project implementation.
Finance ministry to cut corporate tax for industries, consumer goods in upcoming budget
Bangladesh has received considerable budget support from external sources in recent years, a trend expected to continue in the medium term, the document stated, highlighting the ongoing commitment to leveraging both domestic and international financial strategies to meet fiscal challenges.
1 year ago
'Smart Bangladesh' by 2041: Government undertakes 8 strategic initiatives
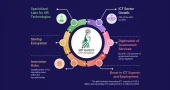
The government of Bangladesh has undertaken eight strategic initiatives aimed at transforming the nation into a cost-effective, sustainable, innovative, intelligent, and knowledge-based 'Smart Bangladesh' by 2041.
These initiatives are designed to enhance the ICT sector's contribution to the GDP, expand digital services, and foster innovation across various domains.
Key Initiatives and Targets
ICT Sector Growth: The government aims for the ICT sector to contribute 20 percent to the GDP by 2041. This ambitious target is part of a broader strategy to diversify the nation's economic foundations.
Digitization of Government Services: By 2041, 100 percent of government services will be digitized, making them more accessible to the populace. This effort seeks to streamline processes and enhance the efficiency of public service delivery.
Boost in ICT Exports and Employment: The plan includes increasing ICT exports to USD 5 billion and expanding ICT employment to 3 million by 2025. Additionally, professional mentorship will be provided to 1,000 Bangladeshi startups by 2025 to nurture emerging entrepreneurs.
Innovation Hubs: Establishment of 10 innovation hubs within the top universities aims to stimulate creativity and technological advancement.
Startup Ecosystem: The goal to build at least 5 unicorns—startups valued at over USD 1 billion—reflects the government's commitment to fostering a robust startup ecosystem.
Specialized Labs for 4IR Technologies: Universities will host specialized labs focusing on cutting-edge technologies such as Robotics, AI, IoT, Big Data, Blockchain, and AR/VR, preparing students for future job markets.
Smart Digital Leadership Academy and 4IR Centre: These institutions will play pivotal roles in cultivating leadership and technical skills necessary for the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Read more: Govt to include Smart Bangladesh in mid-term dev plan: Official Document
Current Progress and Future Plans
With over two-thirds of Bangladesh's population in the workforce, skill development and employment generation, particularly in the ICT sector, are high priorities. The government is actively transforming its large workforce to meet future market demands, as evidenced by the slight decrease in unemployment from 4.2 percent in FY 2016-17 to 3.6 percent in 2022, according to the Labor Force Survey 2022.
Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina recently highlighted that the unemployment rate is at three percent. Efforts to decrease this further include the Skills for Employment Improvement Program, implemented by the Finance Division, under which over 600,000 individuals have been trained.
Furthermore, the successful implementation of various initiatives has already facilitated employment for about 2 million people in fields ranging from IT freelancing to fintech and e-commerce, according to the official document ‘Medium Term Macroeconomic Policy Statement (2023-24 to 2025-26)’. The Bangladesh Hi-tech Park Authority is also working to convert over 60,000 youths into IT professionals by 2025, with 37,800 already having completed training programs, the document added.
Read more: Join hands in building ‘Smart Bangladesh’ under PM Sheikh Hasina's leadership: Envoy
Looking Ahead
The ICT Division has formulated the "Smart Bangladesh: ICT 2041 Master Plan" centered around four pillars: Smart Citizen, Smart Government, Smart Economy, and Smart Society. These pillars are expected to guide Bangladesh to the next stage of development, leveraging the potential of the 4IR to achieve a smarter and more sustainable future.
The initiatives reflect a comprehensive strategy by the Bangladesh government to harness the power of digital technology and innovation, steering the country toward significant economic transformation and enhanced global competitiveness by 2041.
Read more: Palak delivers speech on Smart Bangladesh in Singapore
1 year ago
Bangladesh earmarks Tk 385 billion for agriculture, aiming for 10% annual growth by fiscal 2026
The Bangladesh government has earmarked Tk 385 billion for agricultural development over the next three years, targeting an average annual growth of 10% in the sector by the 2025-26 fiscal year.
This investment underscores agriculture's pivotal role in achieving food security and driving equitable economic growth, according to the 'Medium Term Macroeconomic Policy Statement (2023-24 to 2025-26)'.
Despite a diminishing share in GDP, agriculture remains critical for the livelihood of the majority, particularly in rural areas. To boost food production and resilience against adversities, the government's strategy includes developing high-yield and adversity-tolerant crop varieties, expanding mechanization and irrigation, and improving access to affordable inputs like seeds and fertilizers.
No respite from heat wave in five days: BMD
The policy document highlights several initiatives aimed at modernizing agriculture through technology. These include increasing the use of surface water for irrigation over groundwater to conserve resources, incorporating renewable energy solutions, and employing remote sensing for crop monitoring.
The government also continues to support the sector with subsidies, financial incentives, and technological innovations to foster a sustainable and self-reliant agricultural framework.
Significant contributions also come from the fisheries and livestock sub-sectors, which not only bolster GDP—2.53% and 1.91%, respectively—but also provide essential protein sources and livelihoods for over 12% of the population. Achievements in these areas include self-sufficiency in fish, meat, and egg production, with milk expected to follow. Moreover, these sectors are vital for foreign exchange earnings through exports.
Looking ahead, the Ministry of Livestock and Fisheries is set to launch development projects to enhance production capacities, adopt advanced management technologies, and improve conservation efforts, particularly for young hilsa fish ('jatka').
Water resource management is another focal area, given its importance to sustainable agriculture. Initiatives are underway to improve surface water availability through the excavation of water bodies and the enhancement of coastal afforestation, aiming to secure equitable water shares from transboundary rivers.
NAP Expo 2024: Bangladesh to showcase climate adaptation success, Environment Minister says
Amid threats of substantial economic losses due to climate change—projected at a 6.8% reduction in GDP by 2030—the government has prioritized comprehensive strategies to mitigate these impacts. The Mujib Climate Prosperity Plan is designed to equip vulnerable sectors and communities with the tools to enhance resilience and stability against climate-related disruptions.
Through these multifaceted efforts, Bangladesh is taking decisive steps to not only safeguard but also advance its agricultural heritage in the face of evolving global challenges.
1 year ago